An Information System is an interconnected set of components used to collect, store, process and transmit data and digital information. It is a collection of hardware, software, network, data, people and process that work together to transform raw data into useful information.
Types of Information System
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS):TPS handles routine transactions such as order processing, payroll, and inventory management. It ensures accurate and timely recording of transactions.
Management Information Systems (MIS):MIS provides managers with reports and information to support decision-making and operational activities. It aggregates data and presents it in a summarized and structured format.
Few More Types are such as Decision support system, knowledge management system, office automation system etc.
2.Why do we need Information System?
1->An Is Support various variety of business objective such as improved customer service and improve efficiency.
2-> An IS, focuses on how people use it and data to manage and make decisions within an organization.
3-> IS supports knowledge management and communication.
4-> IS also support in various business functions such as accounting, finance, marketing, human resources, operations and supply chain management.
5-> It gives an opportunities in e-commerce, social media and artificial intelligence.
3.Explain the threats of information security?
Information Security threats can be many like Software attacks, theft of intellectual property, identity theft, theft of equipment or information, sabotage, and information extortion.
Threat can be anything that can take advantage of a vulnerability to breach security and negatively alter, erase, harm object or objects of interest.
Software attacks means attack by Viruses, Worms, Trojan Horses etc. Many users believe that malware, virus, worms, bots are all same things. But they are not same, only similarity is that they all are malicious software that behaves differently.
Malware is a combination of 2 terms- Malicious and Software. So Malware basically means malicious software that can be an intrusive program code or anything that is designed to perform malicious operations on system.
* What is Malware? Explain its types?
Malware is a combination of 2 terms- Malicious and Software. So Malware basically means malicious software that can be an intrusive program code or anything that is designed to perform malicious operations on system. Malware can be divided in 2 categories:
Infection MethodsMalware Actions
Malware on the basis of Infection Method are following:
Virus – They have the ability to replicate themselves by hooking them to the program on the host computer like songs, videos etc and then they travel all over the Internet. The Creeper Virus was first detected on ARPANET. Examples include File Virus, Macro Virus, Boot Sector Virus, Stealth Virus etc.Worms – Worms are also self-replicating in nature but they don’t hook themselves to the program on host computer. Biggest difference between virus and worms is that worms are network-aware. They can easily travel from one computer to another if network is available and on the target machine they will not do much harm, they will, for example, consume hard disk space thus slowing down the computer.Trojan – The Concept of Trojan is completely different from the viruses and worms. The name Trojan is derived from the ‘Trojan Horse’ tale in Greek mythology, which explains how the Greeks were able to enter the fortified city of Troy by hiding their soldiers in a big wooden horse given to the Trojans as a gift. The Trojans were very fond of horses and trusted the gift blindly. In the night, the soldiers emerged and attacked the city from the inside.Their purpose is to conceal themselves inside the software that seem legitimate and when that software is executed they will do their task of either stealing information or any other purpose for which they are designed.They often provide backdoor gateway for malicious programs or malevolent users to enter your system and steal your valuable data without your knowledge and permission. Examples include FTP Trojans, Proxy Trojans, Remote Access Trojans etc.Bots –: can be seen as advanced form of worms. They are automated processes that are designed to interact over the internet without the need for human interaction. They can be good or bad. Malicious bot can infect one host and after infecting will create connection to the central server which will provide commands to all infected hosts attached to that network called Botnet.
Malware on the basis of Actions:
Adware – Adware is not exactly malicious but they do breach privacy of the users. They display ads on a computer’s desktop or inside individual programs. They come attached with free-to-use software, thus main source of revenue for such developers. They monitor your interests and display relevant ads. An attacker can embed malicious code inside the software and adware can monitor your system activities and can even compromise your machine.Spyware – It is a program or we can say software that monitors your activities on computer and reveal collected information to an interested party. Spyware are generally dropped by Trojans, viruses or worms. Once dropped they install themselves and sits silently to avoid detection.One of the most common example of spyware is KEYLOGGER. The basic job of keylogger is to record user keystrokes with timestamp. Thus capturing interesting information like username, passwords, credit card details etc.Ransomware – It is type of malware that will either encrypt your files or will lock your computer making it inaccessible either partially or wholly. Then a screen will be displayed asking for money i.e. ransom in exchange.Scareware – It masquerades as a tool to help fix your system but when the software is executed it will infect your system or completely destroy it. The software will display a message to frighten you and force to take some action like pay them to fix your system.Rootkits – are designed to gain root access or we can say administrative privileges in the user system. Once gained the root access, the exploiter can do anything from stealing private files to private data.Zombies – They work similar to Spyware. Infection mechanism is same but they don’t spy and steal information rather they wait for the command from hackers.4.Explain the term- information assurance?
“Assurance” in security engineering is defined as the degree of confidence that the security needs of a system are satisfied.Information assurance (IA) is the practice of assuring information and managing risks related to the use, processing, storage and transmission of information. Information assurance includes protection of the integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation and confidentiality of user data.
5.What is risk analysis? Explain the types of risk analysis
Risk analysis is the process of identifying and analyzing potential issues that could negatively impact key business initiatives or projects. This process is done to help organizations avoid or mitigate those risks.
Performing a risk analysis includes considering the possibility of adverse events caused by either natural processes, such as severe storms, earthquakes or floods, or adverse events caused by malicious or inadvertent human activities. An important part of risk analysis is identifying the potential for harm from these events, as well as the likelihood of their occurrence.
Types of risk analysis
Risk analysis comes in different forms, and organizations use various analysis tools, depending on their needs and requirements.
Companies typically use the following risk analysis methods:
Risk-benefit analysis. Typically used for decision-making in the healthcare and environmental sectors, this type of risk analysis weighs the prospective benefits and risks of a choice or course of action. The main goal of this risk-benefit analysis is to make rational decisions by determining whether the potential benefits of a decision outweigh the potential risks, or vice versa.Business impact analysis (BIA). ABIAevaluates the possible effects of disruptions to crucial business processes. Organizations can use this study to determine which procedures are most crucial to their business operations and create backup plans to lessen the effects of disruptions andensure business continuityin the wake of disasters.Needs assessment analysis. Aneeds assessmentis a step-by-step method of determining what a business needs and where it's deficient or not doing so well. It helps leaders see where things could be improved and shows them how to use their resources to reach goals faster.Root cause analysis. Aroot cause analysispinpoints the underlying reasons behind a specific problem, issue or undesirable outcome. While other risk analyses predict future events or possibilities, a root cause analysis focuses on uncovering the main causes behind the problems and understanding the effects of past and ongoing events.
6.What do you mean by application? What are the types of application security?
An application, also referred to as an application program or application software, is a computer software package that performs a specific function directly for an end user or, in some cases, for another application. An application can be self-contained or a group of programs.
Types of application security
Different types of application security features include authentication, authorization, encryption, logging, and application security testing. Developers can also code applications to reduce security vulnerabilities.
Authentication: When software developers build procedures into an application to ensure that only authorized users gain access to it. Authentication procedures ensure that a user is who they say they are. This can be accomplished by requiring the user to provide a user name and password when logging in to an application. Multi-factor authentication requires more than one form of authentication—the factors might include something you know (a password), something you have (a mobile device), and something you are (a thumb print or facial recognition).Authorization: After a user has been authenticated, the user may be authorized to access and use the application. The system can validate that a user has permission to access the application by comparing the user’s identity with a list of authorized users. Authentication must happen before authorization so that the application matches only validated user credentials to the authorized user list.Encryption: After a user has been authenticated and is using the application, other security measures can protect sensitive data from being seen or even used by a cybercriminal. In cloud-based applications, where traffic containing sensitive data travels between the end user and the cloud, that traffic can be encrypted to keep the data safe.Logging: If there is a security breach in an application, logging can help identify who got access to the data and how. Application log files provide a time-stamped record of which aspects of the application were accessed and by whom.Application security testing: A necessary process to ensure that all of these security controls work properly.
7.What is cyber-attacks? Explain the types of cyber-attacks.
A cyber attack is any malicious attempt to gain unauthorized access to a computer, computing system or computer network with the intent to cause damage. Cyber attacks aim to disable, disrupt, destroy or control computer systems or to alter, block, delete, manipulate or steal the data held within these systems.
There are two types of Cyber attacks:
1 Web Based Attacks
2 System Based Attacks
Web Based Attacks=>
1. Injection attacks
It is the attack in which some data will be injected into a web application to manipulate the application and fetch the required information.
Example- SQL Injection, code Injection, log Injection, XML Injection etc.
2. DNS Spoofing
DNS Spoofing is a type of computer security hacking. Whereby a data is introduced into a DNS resolver's cache causing the name server to return an incorrect IP address, diverting traffic to the attacker?s computer or any other computer. The DNS spoofing attacks can go on for a long period of time without being detected and can cause serious security issues.
3. Session Hijacking
It is a security attack on a user session over a protected network. Web applications create cookies to store the state and user sessions. By stealing the cookies, an attacker can have access to all of the user data.
4. Phishing
Phishing is a type of attack which attempts to steal sensitive information like user login credentials and credit card number. It occurs when an attacker is masquerading as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication.
examples-> Brute force, denial of Service, Volume-based attacks, protocol attacks.
System attacks:
1. Virus
It is a type of malicious software program that spread throughout the computer files without the knowledge of a user. It is a self-replicating malicious computer program that replicates by inserting copies of itself into other computer programs when executed. It can also execute instructions that cause harm to the system.
2. Worm
It is a type of malware whose primary function is to replicate itself to spread to uninfected computers. It works same as the computer virus. Worms often originate from email attachments that appear to be from trusted senders.
3. Trojan horse
It is a malicious program that occurs unexpected changes to computer setting and unusual activity, even when the computer should be idle. It misleads the user of its true intent. It appears to be a normal application but when opened/executed some malicious code will run in the background.
4. Backdoors
It is a method that bypasses the normal authentication process. A developer may create a backdoor so that an application or operating system can be accessed for troubleshooting or other purposes.
5. Bots
A bot (short for "robot") is an automated process that interacts with other network services. Some bots program run automatically, while others only execute commands when they receive specific input. Common examples of bots program are the crawler, chatroom bots, and malicious bots.
8.What is E-commerce? Explain the threats of e-commerce
Ecommerce is a method of buying, selling goods and services online. The definition of ecommerce business can also include tactics like affiliate marketing. You can use ecommerce channels such as your own website, an established selling website like Amazon, or social media to drive online sales.
Threats of E-commerce
The Risk of Fraud
An electronic payment system has a huge risk of fraud. The computing devices use an identity of the person for authorizing a payment such as passwords and security questions. These authentications are not full proof in determining the identity of a person. If the password and the answers to the security questions are matched, the system doesn't care who is on the other side. If someone has access to our password or the answers to our security question, he will gain access to our money and can steal it from us.
The Risk of Tax Evasion
The Internal Revenue Service law requires that every business declare their financial transactions and provide paper records so that tax compliance can be verified. The problem with electronic systems is that they don't provide cleanly into this paradigm. It makes the process of tax collection very frustrating for the Internal Revenue Service. It is at the business's choice to disclose payments received or made via electronic payment systems. The IRS has no way to know that it is telling the truth or not that makes it easy to evade taxation.
The Risk of Payment Conflicts
In electronic payment systems, the payments are handled by an automated electronic system, not by humans. The system is prone to errors when it handles large amounts of payments on a frequent basis with more than one recipients involved. It is essential to continually check our pay slip after every pay period ends in order to ensure everything makes sense. If it is a failure to do this, may result in conflicts of payment caused by technical glitches and anomalies.
E-cash
E-cash is a paperless cash system which facilitates the transfer of funds anonymously. E-cash is free to the user while the sellers have paid a fee for this. The e-cash fund can be either stored on a card itself or in an account which is associated with the card. The most common examples of e-cash system are transit card, PayPal, GooglePay, Paytm, etc.
E-cash has four major components-
Issuers - They can be banks or a non-bank institution.Customers - They are the users who spend the e-cash.Merchants or Traders - They are the vendors who receive e-cash.Regulators - They are related to authorities or state tax agencies.
In e-cash, we stored financial information on the computer, electronic device or on the internet which is vulnerable to the hackers. Some of the major threats related to e-cash system are-
Backdoors Attacks
It is a type of attacks which gives an attacker to unauthorized access to a system by bypasses the normal authentication mechanisms. It works in the background and hides itself from the user that makes it difficult to detect and remove.
Denial of service attacks
A denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a security attack in which the attacker takes action that prevents the legitimate (correct) users from accessing the electronic devices. It makes a network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily disrupting services of a host connected to the Internet.
Direct Access Attacks
Direct access attack is an attack in which an intruder gains physical access to the computer to perform an unauthorized activity and installing various types of software to compromise security. These types of software loaded with worms and download a huge amount of sensitive data from the target victims.
Eavesdropping
This is an unauthorized way of listening to private communication over the network. It does not interfere with the normal operations of the targeting system so that the sender and the recipient of the messages are not aware that their conversation is tracking.
Credit/Debit card fraud
A credit card allows us to borrow money from a recipient bank to make purchases. The issuer of the credit card has the condition that the cardholder will pay back the borrowed money with an additional agreed-upon charge.
A debit card is of a plastic card which issued by the financial organization to account holder who has a savings deposit account that can be used instead of cash to make purchases. The debit card can be used only when the fund is available in the account.
9.Write a short note on EPS.
Earnings per share (EPS) is calculated as a company's profit divided by the outstanding shares of its common stock. The resulting number serves as an indicator of a company's profitability. It is common for a company to report EPS that is adjusted for extraordinary items and potential share dilution.

10.What is the difference between authorization and authentication in cyber security?

11.What is Cryptography and its need?
Cryptography is the science and art of keeping information secret and secure. It's like a sophisticated lock and key system for the digital world, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access and understand sensitive data.
Need of Cryptography
Privacy: It protects our personal information like financial data, medical records, and online communications from unauthorized access.Security: It safeguards critical infrastructure like power grids, banking systems, and government networks from cyberattacks.Authenticity: It ensures the legitimacy of digital documents and transactions, preventing forgery and fraud.Confidentiality: It allows for secure communication between businesses, governments, and individuals even in hostile environments.
12.Explain in briefly the abbreviation CIA and gives examples.
Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals and systems. Encryption plays a crucial role in achieving confidentiality by transforming data into an unreadable format, accessible only with the correct decryption key.
Integrity: Guaranteeing that information remains unaltered and accurate throughout its lifecycle. Cryptographic hash functions help maintain integrity by generating unique digital fingerprints of data, allowing for detection of any unauthorized modifications.
Availability: Keeping information readily accessible to authorized users when needed. Secure systems and cryptographic protocols are designed to prevent denial-of-service attacks and other disruptions that could hinder data access.
Examples of uses
Confidentiality: When you send an encrypted email, the CIA Triad principle ensures that only the intended recipient can read it, protecting the confidentiality of your message.Integrity: When you download a software update, using a digital signature verifies its integrity, ensuring you haven't downloaded a tampered version with malicious code.Availability: When you access your online banking account, secure authentication protocols and encryption technologies ensure that your financial information remains available to you and protected from unauthorized access.
13.Explain the difference between substitution and transition techniques.
both substitution and transposition techniques play crucial roles in scrambling messages to keep them secret. While they both achieve the goal of encryption, they do so in fundamentally different ways:
substitution and transposition techniques can be combined for increased security. For example, the Vigenere cipher combines Caesar cipher with a keyword to create a more complex substitution.
It's important to note that both techniques are considered outdated in modern cryptography due to advancements in computing power and cryptanalysis techniques.
Feature | Substitution Technique | Transposition Technique |
Transformation | Replaces characters | Rearranges characters |
Impact on characters | Changes identity | Changes position |
Strength against frequency analysis | Weak | Moderate |
Weakness | Vulnerable to pattern recognition based on letter usage | Vulnerable to pattern recognition based on letter positions |
14.Explain the difference between AES and DES?

15.Explain the RSA Algorithm in cryptography.
RSA algorithm is an asymmetric cryptography algorithm. Asymmetric actually means that it works on two different keys i.e. Public Key and Private Key. As the name describes that the Public Key is given to everyone and the Private key is kept private.An example of asymmetric cryptography:A client (for example browser) sends its public key to the server and requests some data.The server encrypts the data using the client’s public key and sends the encrypted data.The client receives this data and decrypts it.
16.Explain the process of developing secure information system?
These are as follows:
Identify Threats: Understand who wants your data and why (burglars, spies, etc.).Analyze Risks: Assess the likelihood and impact of potential attacks (fire, siege, etc.).Prioritize Controls: Implement safeguards based on risk, focusing on critical data first (strong gates, guards).Design Secure Architecture: Use secure hardware, software, and network configurations (reinforced walls, hidden tunnels).Implement Access Controls: Limit access to authorized users only (locks, passwords).Encrypt Sensitive Data: Scramble data at rest and in transit (secret codes, hidden messages).Train Users: Educate users on security best practices (spotting intruders, reporting suspicious activity).Monitor and Audit: Continuously track system activity and investigate anomalies (watchtowers, patrols).
17.What is security architecture.
A security architecture is a set of models, methods, and security principles that align with your objectives, keeping your organization safe from cyber threats. Through security architecture, a business’ requirements are translated to executable security requirements. Just like architecture in construction where there is an examination of the property in such factors as climate, soil type, topography, and client preference, so must a security architect understand the network, firewalls, defence, detection systems, and many other factors.

18.Explain the security issues in hardware.
Hardware security is a domain of enterprise security that focuses on protecting all physical devices, machines, and peripherals. This protection can be in the form of physical security such as guards, locked doors, and CCTV cameras. It can also be in the form of a dedicated hardware component, such as an integrated circuit that provides cryptographic functions for protecting the hardware from security vulnerabilities and deflecting attackers.
Supply Chain Compromise:
Malicious actors can infiltrate the hardware supply chain, inserting backdoors or modifying components during manufacturing. This can compromise entire device ecosystems before they even reach consumers.
2. Side-Channel Attacks:
These attacks exploit unintended leaks of information from hardware like power consumption, electromagnetic radiation, or timing variations. Attackers can analyze these leaks to extract sensitive data like encryption keys.
3. Firmware Vulnerabilities:
Firmware, the low-level code that controls hardware, can contain vulnerabilities that allow attackers to gain control of the device. Updating firmware can be difficult or impossible, leaving devices exposed for extended periods.
4. Tampering and Physical Hacking:
Skilled attackers can physically modify hardware components to extract data, plant malware, or bypass security measures. This can happen through invasive techniques like chip-level analysis or more subtle methods like manipulating external ports.Lack of Transparency and standardization
19.Write a short note on Data storage and downloadable devices.
The storage unit is a part of the computer system which is employed to store the information and instructions to be processed. A storage device is an integral part of the computer hardware which stores information/data to process the result of any computational work.
storage device is hardware that is used for storing, porting, or extracting data files. It can also store information/data both temporarily and permanently.
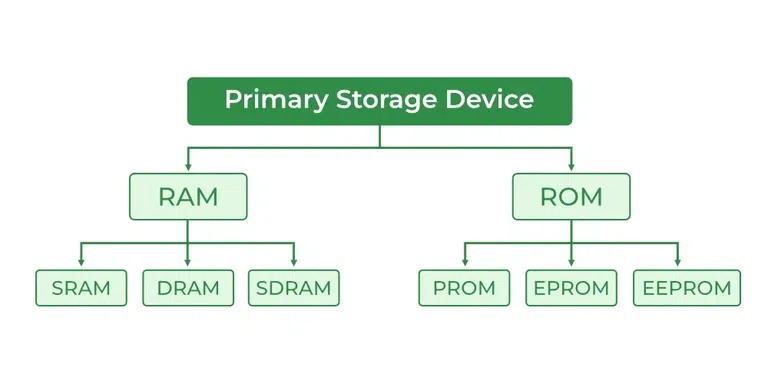
Types of Computer Memory
1. Primary Memory: It is also known as internal memory and main memory. This is a section of the CPU that holds program instructions, input data, and intermediate results. It is generally smaller in size. RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) are examples of primary storage.
2. Secondary Memory: Secondary storage is a memory that is stored external to the computer. It is mainly used for the permanent and long-term storage of programs and data. Hard Disks, CDs, DVDs, Pen/Flash drives, SSD, etc, are examples of secondary storage.
Downloadable devices: Portable devices used to transfer data between systems or store data offline.
USB flash drives: Compact and convenient for small-scale data transfers.External hard drives: Offer larger storage capacities for backups or bulk data movement.Solid-state drives (SSDs): Faster data transfer speeds than traditional hard drives, ideal for frequent data movement.Memory cards: Used in cameras, smartphones, and other devices for storage and data transfer.
20.Write a short note on access control and CCTV.
Access control is a security measure that regulates who or what can view or use resources in a computing environment. It is a crucial aspect of information security that aims to restrict unauthorized individuals or systems from accessing sensitive data, systems, or physical locations. Access control systems typically involve authentication, authorization, and accountability mechanisms.Authentication: This process ensures that the user or system attempting to access a resource is who or what it claims to be. It commonly involves the use of usernames, passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication methods.Authorization: Once authenticated, users or systems are granted specific permissions or privileges based on their roles or attributes. Authorization ensures that individuals only have access to the resources necessary for their roles.Accountability: Access control systems maintain logs and records of user activities, providing accountability and traceability. In the event of security incidents or breaches, these logs help in investigating and understanding the nature of the unauthorized access.
Effective access control is vital in protecting sensitive information, preventing unauthorized modifications, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
CCTV (Closed-Circuit Television):
CCTV refers to a system of video cameras that transmit signals to a specific set of monitors, typically for surveillance and security purposes. These systems are widely used in various settings, including public spaces, businesses, and residential areas, to monitor and record activities. Key components of CCTV systems include cameras, monitors, recording devices, and a network for transmitting signals.
Deterrence: The presence of visible CCTV cameras acts as a deterrent to potential criminal activities. Knowing they are being monitored, individuals are less likely to engage in unlawful behavior.Surveillance: CCTV systems provide real-time monitoring of activities in designated areas. This surveillance helps in detecting and responding to security incidents promptly.Evidence: Recorded footage from CCTV cameras serves as valuable evidence in investigations of security breaches, accidents, or criminal activities. It aids law enforcement and authorities in identifying perpetrators and understanding the sequence of events.Safety: In addition to security, CCTV is also used for safety purposes, such as monitoring industrial processes, traffic control, and emergency response.
21.Define IT ACT?
The term "IT Act" commonly refers to the Information Technology Act, which is a comprehensive legislation enacted in India to address legal issues related to electronic transactions, digital signatures, and cybercrimes. The Information Technology Act, 2000, often abbreviated as the IT Act, was introduced to provide legal recognition and facilitate electronic governance.
22.Define Copyright act.
A Copyright Act is a legal framework that outlines the rights and protections granted to creators of original works, known as copyright holders, in relation to their creative expressions. These acts are enacted by governments to regulate the use, reproduction, distribution, and public display of intellectual property to ensure that creators are granted exclusive rights to their work for a certain period.
23.Define Patent law.
Patent law is a legal framework that grants inventors exclusive rights to their inventions, providing them with a temporary monopoly on the use, manufacturing, and sale of their inventions. The primary purpose of patent laws is to encourage innovation by providing inventors with incentives to disclose their inventions to the public in exchange for exclusive rights for a limited period.
24. Explain intellectual property law.
Intellectual property law grants exclusive rights to creators and inventors over their intangible creations or inventions, protecting works such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. It aims to encourage innovation and creativity by providing legal frameworks for the ownership, use, and protection of intellectual assets.
25.Write a short note on Software license
A software license is a legal agreement between the software copyright holder (licensor) and the end-user (licensee), outlining the terms and conditions under which the software can be used, distributed, and managed. It defines the scope of use, permissions, restrictions, and often includes details about support, updates, and intellectual property rights. Users must adhere to the terms specified in the license agreement to legally use the software. Various types of licenses exist, including proprietary, open source, and freeware licenses, each with distinct terms and implications for users.
